Trauma and Fracture
Medical Laboratory And Specialists Services
Medical Laboratory And Specialists Services
Understanding Fracture Treatments
A. Non-Surgical Fracture Treatments
Casting
Casting involves applying a rigid or semi-rigid plaster or fibreglass cast around the fractured bone to immobilize it and allow the bones to heal in the correct position. This may involve closed reduction of fracture (putting the fracture in place under anaesthesia) and putting a cast on. This method is commonly used for stable fractures, such as those in the arm or leg, and provides support and protection during the healing process.
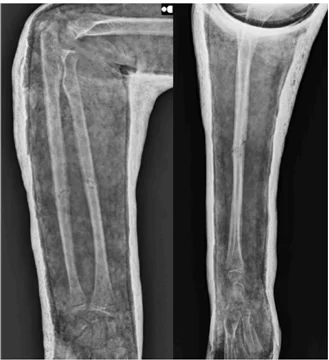
(Closed reduction and casting done for forearm fracture)
Splinting:
Splinting involves using a padded device, typically made of plaster, fibreglass, or metal, to provide support and immobilization to a fractured bone. Splints are often used for initial stabilization before a cast is applied or as an alternative for certain types of fractures that do not require full casting.
Functional Bracing:
Functional bracing involves using specialized braces or orthotic devices that allow controlled movement of the fractured bone while providing stability and support. These braces are commonly used for fractures that require early mobilization or for fractures that have undergone surgical fixation. Braces can also be used to protect the patient in late stages of healing but allow earlier return to function.
B. Surgical Fracture Treatments
In cases where fractures are severe, unstable, or unresponsive to non-surgical treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical fracture treatments aim to realign the broken bone fragments, restore stability, and promote optimal healing. Common surgical techniques for fracture treatment include:
Closed Reduction and Internal fixation (CRIF):
Closed reduction involves aligning the fracture into place without opening at the fracture site. The surgeon under C-arm guidance reduces the fracture in place. The fracture may often be fixed in place with the help of wires, plate, screw, or rods and does involve an incision if needed.
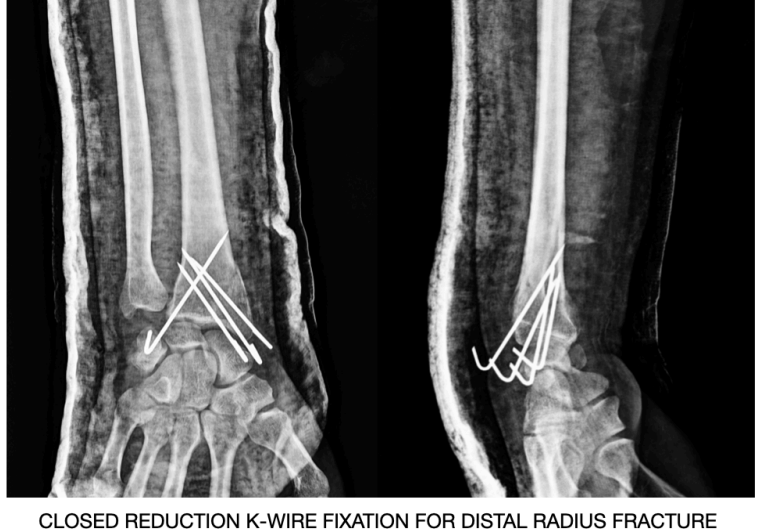
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF):
ORIF involves making an incision to access the fracture site and realigning the bone fragments. Internal fixation devices such as screws, plates, rods, or wires are then used to hold the bone fragments in place during the healing process. This surgical technique provides stability, facilitates proper alignment, and allows for early mobilization.
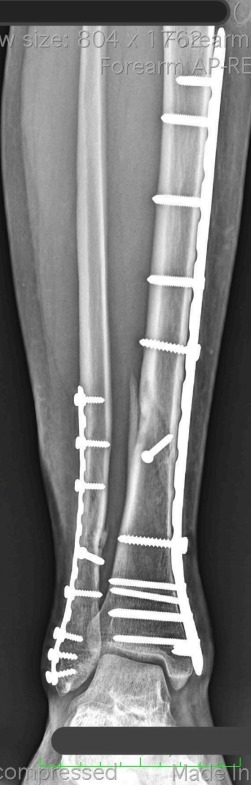 (An example of open reduction and internal fixation with plating done for lower tibia and fibula fracture)
(An example of open reduction and internal fixation with plating done for lower tibia and fibula fracture)
External Fixation:
External fixation involves placing pins or screws into the bone fragments above and below the fracture site. These pins or screws are then connected to an external frame that stabilizes the fracture externally. External fixation is commonly used in complex fractures, fractures with soft tissue damage, or fractures that require gradual realignment. They can also be used as temporary fixation devices till definitive fixation can be done.
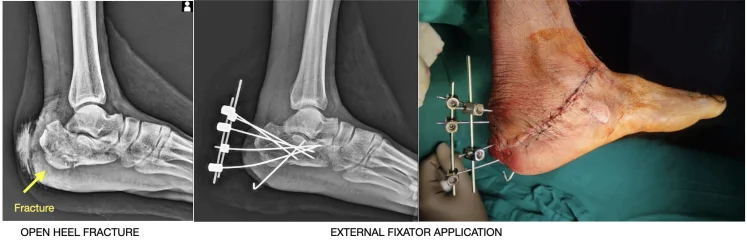
Intramedullary Nailing:
Intramedullary nailing is a technique used for long bone fractures, such as those in the femur or tibia. It involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary canal of the bone to provide stability and promote alignment. This technique allows for early weight-bearing and faster healing.
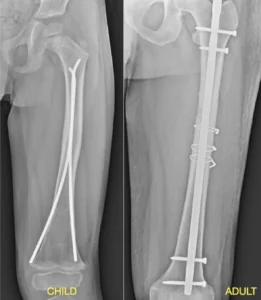 (Intrameduallary nailing in child and adult)
(Intrameduallary nailing in child and adult)
Importance of Prompt Intervention
Prompt medical intervention is crucial in the treatment of fractures. Seeking immediate medical attention after a suspected fracture is vital to ensure accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and optimal outcomes. Delayed or untreated fractures can lead to complications such as malunion (improper healing), nonunion (failure of bones to heal), deformities, and long-term functional limitations. Timely intervention allows healthcare professionals to implement the most suitable treatment plan, which may include non-surgical or surgical methods, depending on the type and severity of the fracture.
Treatment options are customised for each patient based on factors such as age, the severity of the fracture, functional requirements, and the time elapsed since the injury
What are the benefits of Fracture Treatments?
Fracture treatments offer a range of benefits to patients:
Alignment and Stability:
Fracture treatments, whether non-surgical or surgical, aim to realign the broken bone fragments and restore stability. Proper alignment and stability are crucial for optimal healing and prevention of long-term complications.
Pain Relief:
Fractures often cause significant pain and discomfort. Fracture treatments help alleviate pain by immobilizing the affected area, reducing movement, and promoting healing.
Restoration of Function:
Fracture treatments facilitate the restoration of function
and mobility. They allow patients to regain strength, range of motion, and independence, enabling them to return to their daily activities and hobbies.
Prevention of Complications:
Timely and appropriate fracture treatments minimize
the risk of complications such as malunion, nonunion, joint stiffness, and deformities.
By promoting proper healing and alignment, fracture treatments reduce the likelihood of long-term issues.
Psychological Well-being:
Fractures can impact an individual’s psychological well-being, causing emotional distress and limitations in daily life. Effective fracture treatments relieve pain, restore function, and contribute to overall psychological well-being, promoting a positive outlook and improved quality of life.
Why should you opt for it?
Fracture treatments play a vital role in restoring bone health, function, and quality of life for individuals who have experienced fractures. Whether through non-surgical methods or surgical interventions, these treatments aim to realign fractured bones, promote proper healing, and enable patients to regain mobility and independence.
Here at Dr. Bansals Arogya Hospital, our dedicated team of orthopaedic specialists possesses the expertise, experience, and commitment to excellence necessary for effective fracture management. With a patient-centered approach and advanced facilities, we strive to provide comprehensive care that addresses each patient’s unique needs and facilitates a successful recovery.
If you have experienced a fracture, it is crucial to seek timely medical attention. Contact us to schedule a consultation with our orthopaedic team, who will guide you through the treatment options, explain the procedures, and develop a personalized plan for your fracture management. Trust in our expertise and experience to restorey bone health, function, and overall well-being.
